System Unit Explained - Power and Motherboard
As a future IT support specialist, we need to identify the different parts of a computer that we will be assembling, repairing or upgrading. It is necessary for us to identify its name and its function.
In this lesson, we will discuss the different parts of a computer's system unit.
The System Unit is the overall structure that houses the processor, memory, and electronic components of the computer that are used to process data. All input and output devices are connected into the system unit. The system unit is housed by what is known as system case or computer case. It holds and protects most components of a computer.

Image courtesy of freepik
The Computer Case contains the framework to support and enclose internal components of the computer. It helps to prevent damage from static electricity. It typically made up of plastic, steel, and aluminum which are available in a variety of styles. The size and layout of a case is called a form factor. It is also designed to keep internal components cool by using airflow vents and cooling fans.
-
Power Supply

Power supplies serve as the source for electricity to the computer. Attached are vital hardware cables and buses for transferring power to various components in the computer.
- ATX 24 pin main power connector is the standard motherboard power connector used in nearly every computer.
- SATA 15 pin power supply connector is one of several standard peripheral power connectors. SATA power connectors only connect to SATA drives like hard drives and optical drives. SATA power connectors do not work with older PATA devices.
- Molex 4 pin power supply connector is a standard peripheral power connector. Molex power connectors connect to many different kinds of internal peripherals including PATA hard drives and optical drives, some video cards, and even some other devices.
- Floppy drive 4 pin power supply connector is the standard floppy drive power connector. The floppy power connector, also called a Berg connector or Mini-Molex connector, is included in even the newest power supplies even though floppy drives are becoming obsolete.
- ATX 4 pin power supply connector is a standard motherboard power connector used to provide +12 VDC to the processor voltage regulator. This small connector usually attaches to the motherboard near the CPU.
- ATX 6 pin power supply connector is a motherboard power connector used to provide +12 VDC to the processor voltage regulator but the 4-pin variety is the more commonly used connector. This small connector usually attaches to the motherboard near the CPU.
The following are the basic connector you can see in a power supply:
-
Motherboard
The motherboard is the backbone that ties the computer's components together at one spot and allows them to talk to each other. Without it, none of the computer pieces, such as the CPU, GPU, or hard drive, could interact. Total motherboard functionality is necessary for a computer to work well. Source: https://www.hp.com/us-en/shop/tech-takes/what-does-a-motherboard-do
Here is an example of a typical motherboard or mobo for short
Take note that the figure that is shown may not be the latest and may differ from each manufacter. One clear example is the PS/2 may no longer be present in new mobo because the USB port are being use to connect to the keyboard and mouse.
There are several components that are attached to the motherboard. These include:
1. Chip – small piece of semiconducting material, where more integrated circuits are embedded. They have standard-sized pin connectors that allows them to be attached to the motherboard.
2. Bus - an electrical path that enables data flow between various system components.
3. Integrated Circuit (IC) – contains microscopic pathways that carry electric current. The IC contains millions of elements such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors. Many different kinds of chips are located in the motherboard
4. Microprocessor – this is the central processing unit on a chip.
Different variety of chip packages:
1. Dual Inline Package (DIP) – this has two parallel rows of pints that attach the chip package to the circuit board
2. Pin Grid Array (PGA) – holds a larger number of pins because the pins are mounted on the surface of the package.
3. Flip Chip-PGA (CF-PGA) Package – higher performance PGA packaging that places the chip on the opposite sides of the pins.
4. Single Edge Contact (SEC) Cartridge – does not use pins but connects to one of the edges in the motherboard.
FORM FACTOR OF MOTHERBOARDS
When we say form factor of motherboards this refer to the size and shape of the board. It describes the different layout of the components inside the mobo. Here are some of the form factors of motherboards
- AT – Advanced Technology
- ATX - Advanced Technology Extended
- Mini-ATX – Smaller footprint of ATX
- Micro-ATX – Smaller footprint of ATX
- LPX – Low-profile Extended
- NLX – New Low-profile Extended
- BTX – Balanced Technology Extended
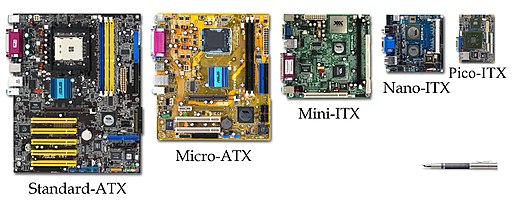
VIA Gallery from Hsintien, Taiwan, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons




Comments
Post a Comment